Strategic Insights into Stock Option Plan Valuation and the Modern Stock Option Incentive Plan
Introduction to Strategic Stock Option Incentive Valuation
As companies compete aggressively for talent, capital efficiency, and long-term shareholder value, equity-based compensation has become one of the most powerful strategic instruments in modern corporate finance. At the center of this transformation stands the stock option incentive plan, supported by rigorous stock option plan valuation methodologies and legally structured through comprehensive frameworks guided by the stock option plan definition. Alongside this, corporate equity participation is increasingly supplemented by structured share acquisition models that raise important questions regarding stock purchase plan taxes, while real-world implementation is best understood through a practical company share option plan example. Together, these systems define how ownership, performance incentives, and enterprise value align in contemporary organizations.
 1. The Strategic Meaning Behind Stock Option Plans
1. The Strategic Meaning Behind Stock Option Plans
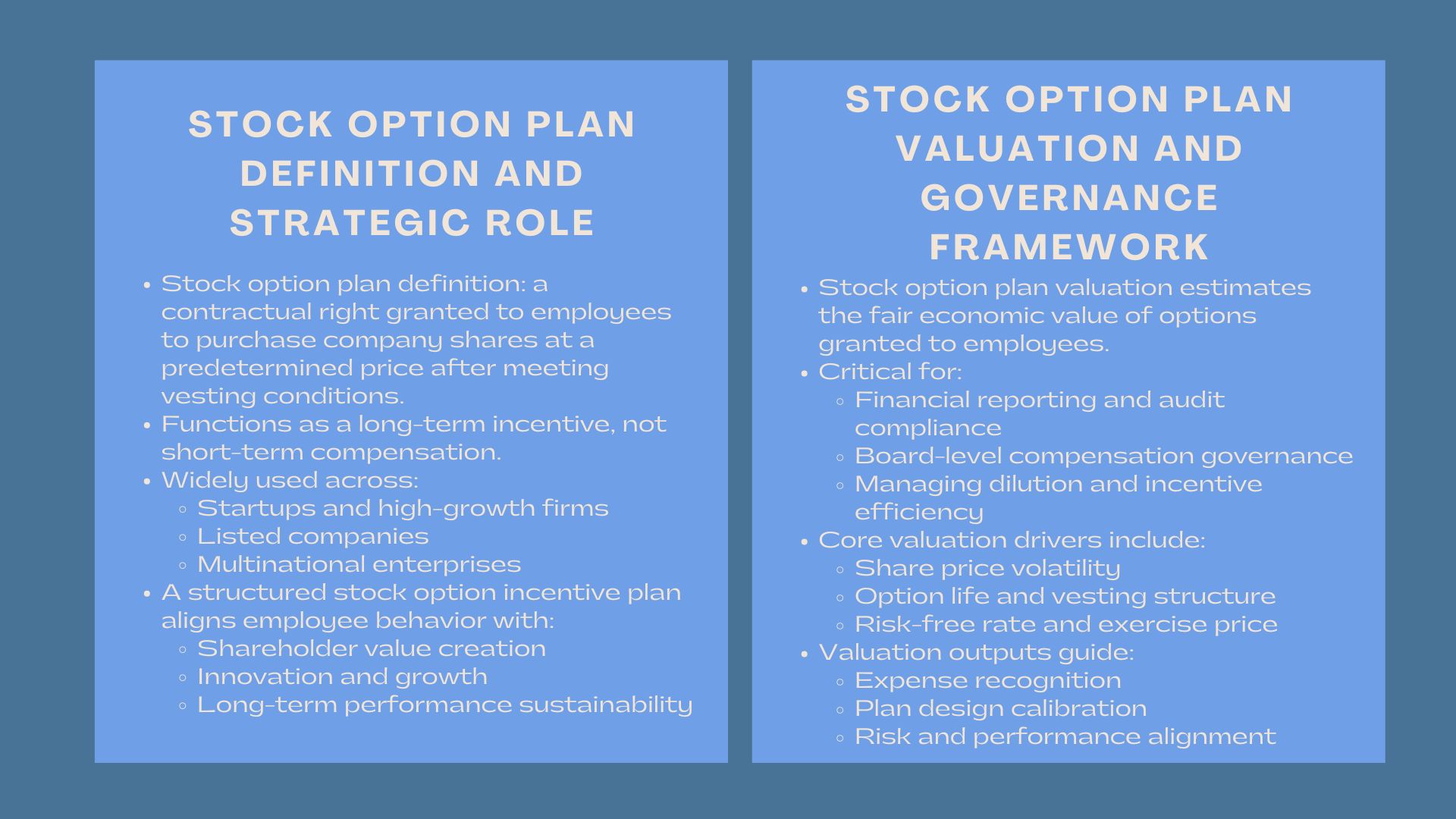
1.1 Understanding the Stock Option Plan Definition
The stock option plan definition refers to a contractual arrangement that grants employees the right, but not the obligation, to purchase company shares at a predetermined price within a specific time frame. This right becomes exercisable only after certain vesting conditions are satisfied. From a financial perspective, the stock option plan definition reflects a forward-looking compensation mechanism that connects employee wealth creation directly to future corporate performance.
This definition has evolved significantly beyond its early use in startups. Today, the stock option plan definition applies across listed corporations, private enterprises, multinational groups, and high-growth technology firms. It serves as both a reward system for past performance and a retention mechanism for future contribution.
1.2 Strategic Role of Equity-Based Compensation
The stock option incentive plan has become a cornerstone of long-term human capital strategy. Unlike cash bonuses that reward short-term results, stock options promote sustained value creation by aligning employee decision-making with shareholder outcomes. This alignment transforms employees into long-term value stewards rather than short-term income maximizers.
A properly structured stock option incentive plan reinforces strategic behaviors such as innovation, revenue scalability, customer retention, and cost discipline. The economic rationale is simple: as enterprise value grows, both shareholders and employees benefit simultaneously.
2. Foundations of Stock Option Plan Valuation
2.1 Why Stock Option Plan Valuation Is Critical
Stock option plan valuation is the analytical process used to estimate the fair economic value of stock options granted under employee compensation schemes. It is a regulatory, financial reporting, and corporate governance necessity. Without proper stock option plan valuation, companies expose themselves to accounting misstatements, tax inefficiencies, and regulatory non-compliance.
From a financial reporting perspective, stock option plan valuation determines compensation expense recognition under accounting standards. From a strategic perspective, it allows boards to assess whether equity incentives are proportionate, competitive, and value-accretive.
2.2 Valuation Inputs and Economic Drivers
The mechanics of stock option plan valuation depend on a combination of share price volatility, expected life of the option, risk-free interest rate, dividend projections, and strike price dynamics. These factors reflect both market uncertainty and firm-specific performance risks.
In practice, stock option plan valuation transforms intangible expectations about growth into quantifiable financial metrics that investors, auditors, and regulators can evaluate with consistency.
3. Structure and Governance of the Stock Option Incentive Plan
3.1 Design Objectives of a Stock Option Incentive Plan
A well-crafted stock option incentive plan balances equity motivation with long-term shareholder protection. It defines eligibility criteria, vesting schedules, exercise conditions, and termination rights. The purpose is to incentivize performance without encouraging excessive risk-taking or short-term financial manipulation.
In global corporations, the stock option incentive plan serves as a strategic retention engine for senior executives, critical technical talent, and leadership successors. When aligned with corporate objectives, the plan supports sustained returns rather than speculative growth.
3.2 Risk Management Through Plan Structuring
Risk exposure within a stock option incentive plan arises when improper strike pricing, short vesting periods, or misaligned performance targets distort decision-making. Therefore, governance committees rely heavily on stock option plan valuation outputs when designing compensation fairness and sustainability thresholds.
4. Practical Insights Through a Company Share Option Plan Example
4.1 Mid-Market Technology Firm Illustration
A realistic company share option plan example can be observed in a mid-sized software development firm expanding internationally. The company establishes a four-year vesting stock option program for engineers, allowing them to purchase shares at today’s valuation after achieving service and performance milestones.
In this company share option plan example, the company uses formal stock option plan valuation to estimate the accounting cost of each grant. As product adoption accelerates, share prices rise significantly above the exercise price. Employees exercise their options at maturity, realizing substantial wealth gains while the company benefits from increased retention and performance continuity.
4.2 Large-Cap Public Company Illustration
In a publicly traded company, a structured company share option plan example involves annual executive grants tied to earnings per share growth, return on equity, and ESG performance indicators. The embedded stock option incentive plan supports capital market confidence while encouraging executives to balance profitability with long-term sustainability.
5. Financial Reporting and Regulatory Compliance
5.1 Accounting Treatment of Stock Option Plans
From an accounting standpoint, stock option plan valuation directly determines the compensation expense recognized over the vesting period. Improper calibration leads to earnings distortions and regulatory scrutiny.
Auditors demand transparent documentation of inputs used in stock option plan valuation, while regulators evaluate whether the stock option plan definition meets disclosure requirements under securities laws.
5.2 Cross-Border Regulatory Challenges
Multinational corporations face additional complexity when implementing a stock option incentive plan across jurisdictions. Variations in securities law, employment regulations, and tax classifications demand jurisdiction-specific interpretations of the same stock option plan definition.
6. Tax Considerations and Stock Purchase Plan Taxes
6.1 Understanding Stock Purchase Plan Taxes
Stock purchase plan taxes arise when employees acquire company shares either through stock options or employee share purchase schemes. The taxable event may occur at grant, vesting, exercise, or sale, depending on jurisdictional tax rules.
In many countries, stock purchase plan taxes are triggered at the moment of exercise when the market price exceeds the strike price. The difference is often treated as employment income and subject to progressive income tax rates.
6.2 Corporate Tax and Employer Obligations
From the corporate perspective, stock purchase plan taxes also impact payroll tax liabilities, employer reporting obligations, and deferred tax balances. These tax effects interact directly with stock option plan valuation, affecting total compensation economics.
7. Investor Perception and Market Valuation Effects
The presence of a transparent stock option incentive plan influences investor confidence directly. Markets interpret equity-based compensation as a signal of management’s confidence in long-term enterprise growth. However, excessive dilution risk from poorly governed plans damages valuation multiples.
A disciplined approach to stock option plan valuation ensures that shareholders can quantify dilution exposure against projected economic benefits. In public equity markets, option issuances are now evaluated alongside capital expenditure efficiency and dividend policy.
8. ESG, Governance, and Executive Accountability
Modern governance frameworks integrate stock option incentive plan metrics within environmental, social, and governance performance evaluation. Linking equity incentives to ethical conduct, carbon reduction, workforce safety, and governance transparency reinforces sustainable enterprise behavior.
In this context, the stock option plan definition evolves from a purely financial mechanism into a governance instrument for stakeholder accountability.
9. Digital Transformation in Stock Option Management
Advanced digital platforms now automate stock option plan valuation, vesting administration, and compliance reporting. Artificial intelligence enhances forecasting accuracy by dynamically updating volatility assumptions, employee exercise behavior, and share liquidity indicators.
Alt text for required SEO image placement: “stock option plan valuation framework illustrating the performance linkage within a stock option incentive plan and the regulatory application of the stock option plan definition.”
These digital systems significantly improve governance precision while lowering compliance costs across multinational operations.
10. Strategic Workforce Planning Through Equity Incentives
As workforce demographics shift toward younger, mobile, and innovation-driven professionals, the stock option incentive plan has become central to employer branding. Equity upside increasingly differentiates top employers within competitive talent markets.
Professionals who understand the stock option plan definition and manage the implications of stock purchase plan taxes can strategically time exercises, diversify risk, and integrate equity wealth into long-term financial planning.
11. Risk Exposure and Concentration Challenges
Despite its advantages, the stock option incentive plan exposes employees to wealth concentration risk. When both income and investment derive from the same employer, adverse corporate performance can simultaneously impact salary and capital.
For this reason, financial advisors emphasize diversification strategies once options are exercised, while boards rely on stock option plan valuation stress testing to forecast downside exposure.
12. Integration with M&A and Corporate Restructuring
During mergers and acquisitions, existing equity plans must be revalued, restructured, or accelerated. Stock option plan valuation becomes a transaction-critical input in purchase price allocation, employee retention structures, and post-merger integration planning.
In many transactions, treatment of unvested options determines executive retention success and long-term deal value realization.
Conclusion
The stock option incentive plan has become one of the most influential instruments of modern corporate finance, seamlessly linking workforce motivation, executive accountability, and shareholder wealth creation. Anchored by rigorous stock option plan valuation, guided by a transparent stock option plan definition, and shaped by evolving rules on stock purchase plan taxes, equity-based compensation now operates as a strategic capital structure component rather than a mere HR policy. Through every practical company share option plan example, the lesson remains consistent: when properly governed, equity incentives transform organizations into high-performance ecosystems where individual success and corporate value growth advance in unison.
