Understanding Business Valuation: A Practical Guide with Workbooks, Tools, and QuickBooks Integration
Introduction to Build Practical Business Valuation Knowledge
Business valuation is no longer a niche exercise reserved for mergers, acquisitions, or litigation. In today’s data-driven and compliance-focused environment, valuation has become an essential management discipline used for strategic planning, financing, taxation, shareholder reporting, and performance measurement. Professionals across finance, accounting, and entrepreneurship increasingly seek clarity in understanding business valuations to make informed decisions that affect enterprise value and long-term sustainability.
This article provides a focused and practical exploration of understanding business valuation, with particular emphasis on applied learning tools and financial systems integration. It examines how structured learning resources such as an understanding business valuation workbook support valuation competence, and how accounting platforms like business valuation quickbooks can be used to enhance data reliability and valuation accuracy. The discussion is designed for business owners, finance professionals, and advisors who require a clear, professional, and applied understanding of valuation in real-world settings.
 1. Understanding Business Valuation as a Core Financial Discipline
1. Understanding Business Valuation as a Core Financial Discipline
1.1 What Understanding Business Valuation Really Means
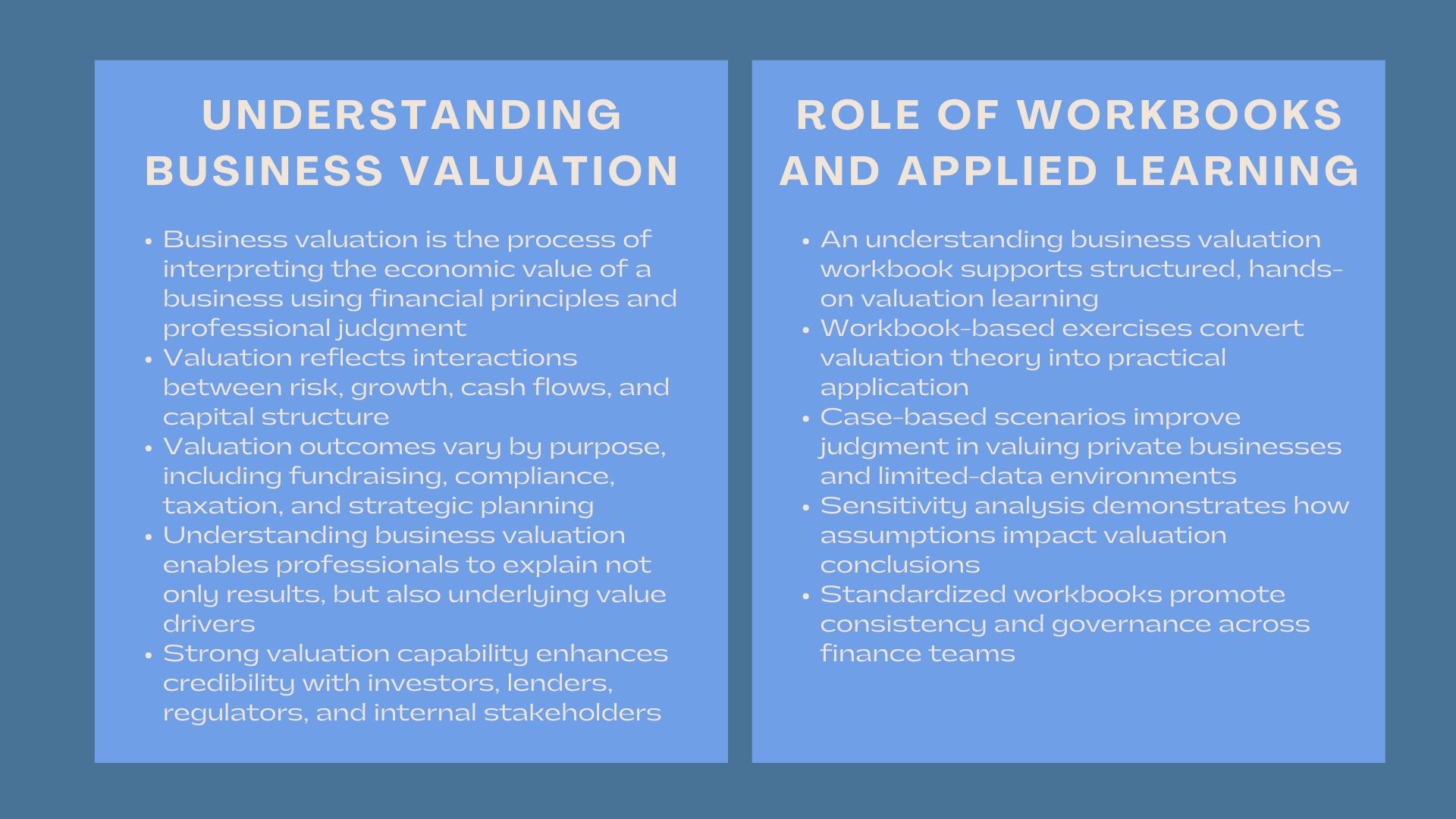
Fundamentally, business valuation implies the capability of interpreting the economic value of a business based on accepted financial principles and assumptions and procedures. It is not just a matter of doing some calculations and it involves understanding the interactions between risk, growth, cash flows and capital structure. When professionals are able to demonstrate high competence in terms of business valuations, they may not only tell how a given valuation came out to be, but also the forces behind a given valuation.
Practically, valuation is a relative issue. A fundraising valuation can be done with an eye on growth potential whilst a regulatory reporting valuation can be driven by conservatism and compliance. That is why it is necessary to prepare the structured ability to comprehend business valuation to make decisions on various business situations, where the decision-makers are involved.
1.2 Why Business Valuation Skills Are Increasingly Critical
The contemporary companies are establishing their operations in a volatile, intangible and regulated environment. Investors and regulators want the management to render value creation with justifiable data and thinking. This has led to the point that interpretation of business valuations has taken a central place in the dexterity of executives, accountants and financial analysts.
To take an example, the owners of small businesses who require external financing should be able to explain what enterprise value is in a clear manner, and the teams that compile internal forecasts need to be sure that the strategic plans and valuation assumptions are consistent. In every situation, the appropriate background in the business valuation enhances the credibility and quality of decision.
2. The Role of Structured Learning in Valuation Mastery
2.1 Understanding Business Valuation Workbook as a Learning Tool
Applied learning resources are one of the most effective in developing the ability of an individual to create valuation. A cognition business valuation workbook has designed exercises, case studies, and practical scenarios, which convert theory into practice. Contrary to a purely scholarly research, a workbook format stimulates the active work with financial data, assumptions, and the logic of valuation.
Awareness of the valuation inputs and their impacts on results is usually enhanced among professionals who are operating under an understanding business valuation workbook. As one example, value conclusions can be observed when the discount rates, terminal growth assumptions or normalized earnings change in a guided learning environment (under a set of assumptions). This practical method plays a substantial role in enhancing the knowledge of business valuation as a practical issue.
2.2 Practical Application Through Case-Based Valuation Exercises
Case-based learning within a business valuation workbook of understanding reflects valuation issues in the real world. Valuations of a privately-owned company having limited market information or differences in book versus economic value can be to be appreciated by learners. These drills strengthen professional judgment that is required in credible knowledge of business valuation.
These workbooks are especially effective in the corporate training setting where finance units need to coordinate the valuation methods between departments. In solving standardized valuation cases, organizations enhance uniformity and regulation on valuation decisions.
3. Integrating Accounting Data into Business Valuation
3.1 Importance of Reliable Financial Data in Valuation
Financial information must be reliable so that accurate valuation is made. Aligning accounting information with the reality of the economy is one of the most popular issues in the interpretation of the business valuation. Compliance financial statements are usually efficient prior to alteration to analysis of valuation.
Structured systems and tools play a very important role here. Accounting systems that maintain a uniform and auditable flow of data can contribute to minimizing errors and enhancing transparency in the inputs of valuations. Good knowledge of business appraisals entails individuals who fill the gap between the accounting documents and assessment models.
3.2 Business Valuation QuickBooks as a Practical Tool
Business valuation quickbooks is plays a major role in financial data management of many small and mid-sized enterprises. QuickBooks offers historical financial statistics, transaction-based detail and reporting capability that can be customized to be used in valuation. Business valuation quickbooks facilitates more earnings and cash flow analysis as it normalizes better when used properly.
When professionals use the system to perform valuation operations, they will find it easy to extract multi-year income statements and balance sheets out of the system. This information is the basis of discounted cash flow, earnings multiples, and scenario testing. Consequently, business valuation is now more factual and justifiable.
4. Linking Accounting, Valuation, and Decision-Making
4.1 Translating Accounting Numbers into Economic Value
The ability to translate the consequences of accounting into economic performance is one of the most difficult issues when learning about business valuations. The accounting standards are concerned with the historical cost and compliance whereas the valuation is concerned with future benefits and risk-adjusted returns. This disavowal can be very confusing to lay people.
The systematic analysis can be used, with the help of such tools as business valuation quickbooks, to detect non-recurring items, normalize the owner compensation, and make adjustments to accounting policies that bias economic reality. These are the adjustments that are vital in proper business valuation.
4.2 Using Valuation to Support Strategic Decisions
Valuation is not a one-sided exercise. Companies with high levels of business valuation enlightenment adopt valuation information in determining pricing methods, share capital, and performance appraisal. In example, valuation analysis would allow the management to determine which between reinvesting profits and acquisitions would result in higher shareholder value.
Here, systems co-exist with work books. Knowledge business valuation workbook inculcates analytical discipline, and business valuation quickbooks is the data foundation of prompt and dependable valuation updates.
5. Common Challenges in Understanding Business Valuations
5.1 Misinterpretation of Valuation Outputs
One of the pitfalls in interpreting the business valuations is to use only one figure of valuation. Valuation is subjective and is prone to assumptions. Stakeholders can take valuation outputs as accurate instead of indicative without sufficient context.
Learning tools like the knowledge of business valuation workbook can be used to overcome this dilemma to focus on scenario-based analysis and sensitivity testing. These instruments support the notion that valuation is a relative measure and not an absolute solution.
5.2 Data Limitations and System Constraints
The other problem is encountered when the accounting systems are not based on valuation. As much as the business valuation quickbooks has a great functionality, it still needs professional judgment in the completion and accuracy of data. Lack of any historical data, discrepancies in classification or inadequate documentation may compromise the credibility of valuation.
Experts who are very aware of business valuation techniques are able to identify such limitations and put in place a control mechanism to reduce the risk of the data. This involves alignment of system records to systems and documentation of valuation adjustments.
6. Building Organizational Capability in Business Valuation
6.1 Training and Professional Development
Companies are putting more resources in valuation training to enhance financial governance. There are structured programs that include an understanding business valuation workbook, which becomes a stable learning environment among the finance teams. Such programs do not just enhance technical competence but also the level of communication between finance, management and other stakeholders.
In the long-run, this investment builds the organizational maturity in terms of gaining knowledge on the business valuation, lessening the use of external advisor services in undertaking routine business valuation tasks and increasing the quality of internal decision.
6.2 Embedding Valuation into Financial Processes
Valuation thinking is incorporated in budgeting, forecasting and in performance management in leading organizations. Through integrating the financial planning and the drivers of value, the management makes sure that the operational decisions are made in ways that add value in the long term. The business valuation quickbooks are tools that facilitate this integration since it allows access to financial data continuously.
This integrated methodology changes the perception of business valuation, which is a period exercise, to a continuous management science.
7. Practical Use Cases Across Business Lifecycles
7.1 Valuation for Growth and Financing
Growth-stage and startups are the ones that are most dependent on the information on business valuation in the course of negotiations with investors. The credibility and the ensuing outcomes of the negotiation would be boosted with a systematic method aided by workbook-based learning and system data.
7.2 Valuation for Succession and Exit Planning
The owners of businesses intending to make a succession or sell them stand to gain by investing in the business valuation earlier. Frequent review of valuation that is backed by business valuation quickbooks enables the owners to determine the value drivers and work on the weaknesses prior to a transaction.
Conclusion
Developing strong capability in understanding business valuations is no longer optional in today’s complex business environment. It requires a combination of conceptual knowledge, practical application, and reliable financial data. Tools such as an understanding business valuation workbook provide structured learning that strengthens analytical judgment, while systems like business valuation quickbooks support data integrity and efficiency.
By integrating these elements, professionals and organizations can achieve a more accurate, transparent, and strategic approach to understanding business valuation. This integrated capability enhances decision-making, improves stakeholder confidence, and supports sustainable value creation across all stages of the business lifecycle.
