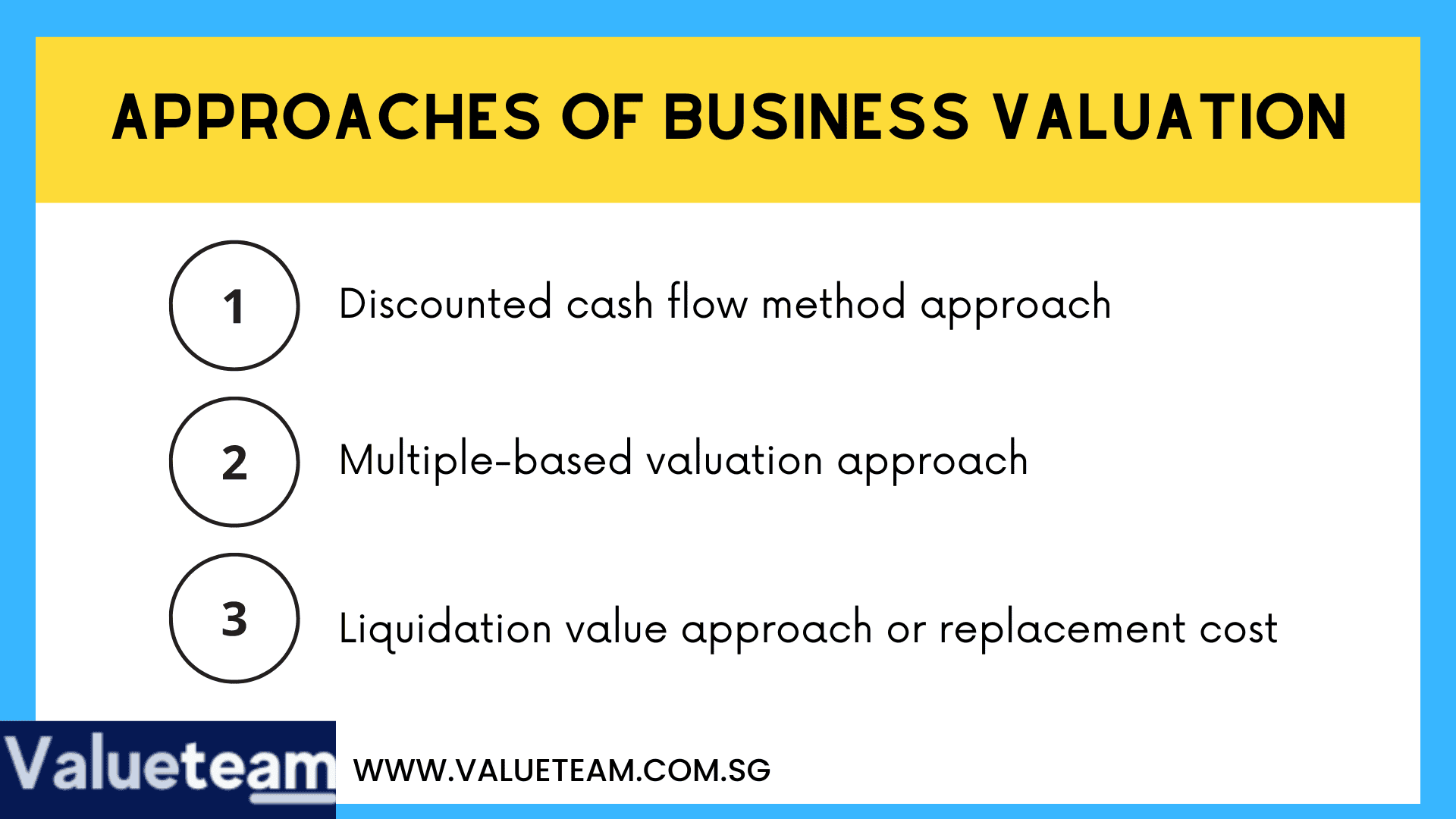
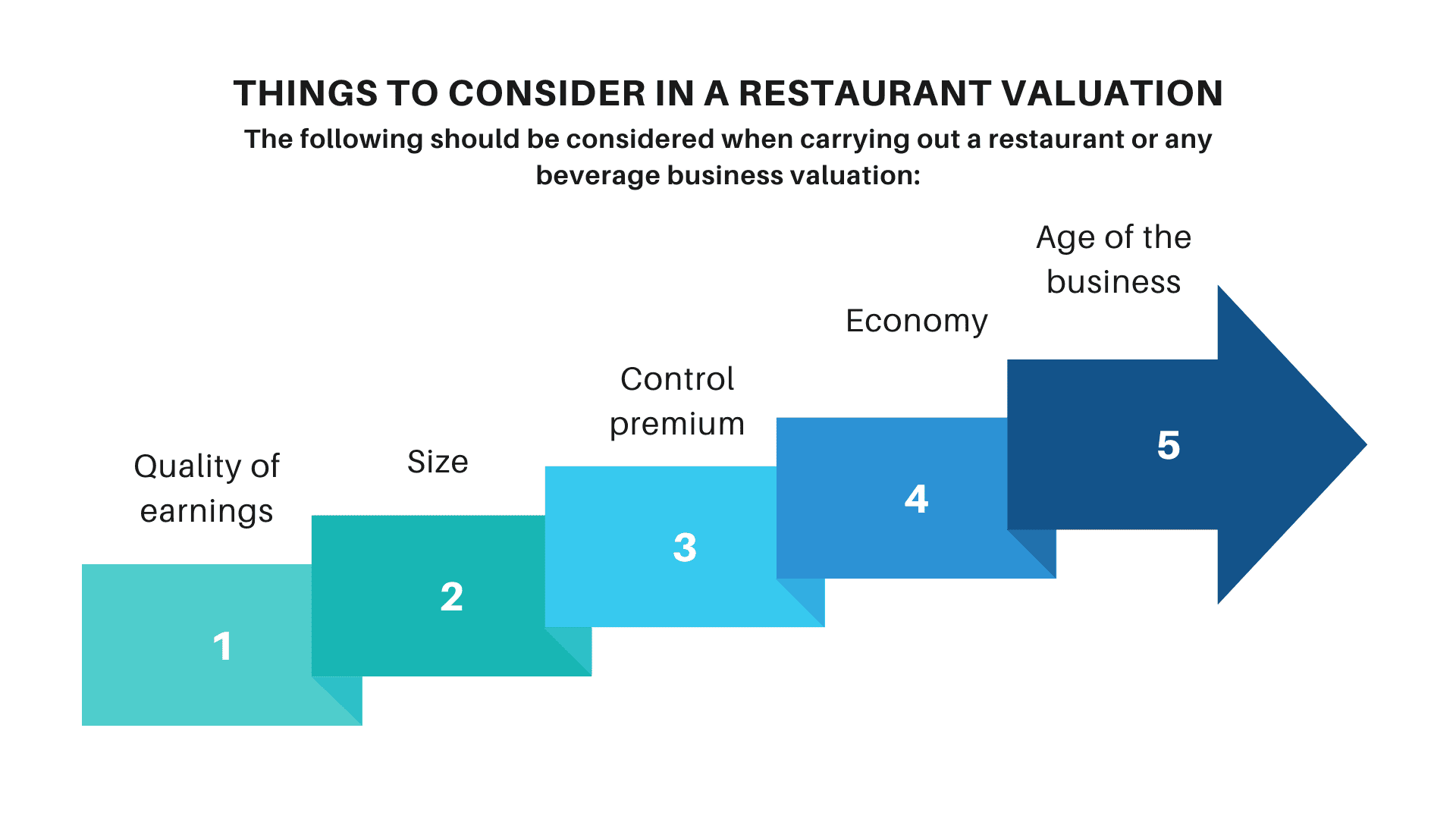This is a general approach used in knowing the value of businesses such as the food and beverage businesses. It is often represented with the acronym – DCF. This business valuation methodology considers the cash flow the company will generate in the future. It also assumes the risks that may be involved with future cash flows.
Typically, this business valuation method is used to confirm or support a business valuation done with the discounted cash flow methodology. Applying competitors multiples is a common approach used.
This approach is also known as replacement cost. When a company has specialized and unique machinery, a buyer can consider the replacement cost of equipment, property, and plant to support every other valuation approach.
The following should be considered when carrying out a restaurant or any beverage business valuation:
1. Quality of earnings
The higher a business earns, the higher the valuation multiple. Also, the lower the company’s earnings result, info lowers the business valuation.
2. Size
The valuation of a large food and beverage business in terms of income streams, diversified products and services, and a low-risk profile is higher than a business that is not large.
3. Control premium
Control premium will be included in the valuation multiple when a buyer acquires over 50% of the shares. This is done to show the control power or right of the business.
4. Economy
The current economy and the market can affect the value of a food business. If the current economy is low, the company’s value will reduce and vice versa. It is better to sell your business when the economy and market are favorable, as it will increase the value of your business.
5. Age of the business
When the business is well established and doing well, an investor will be willing to buy it at a high price. He will do this as he is confident of the returns. Investors are interested in the number of years you have grown the business. They want to know how consistent the company is and if they will be losing when they buy.